Waves of Your Brain
By Kasturi Sinha
The brain-an electrochemical organ in the body-can generate as many as 10 Watts of electrical power. The human scalp can record so much power that it can light an entire light bulb! However, what allows such an excessive amount of power to pass through the neurons? In the human body, there are numerous waves that affect the actions and states the body is in. What are the waves composed of? The neurons in your brain use electricity to communicate. This electricity moves in a wave-like motion which the reason these are known as brain waves.
Brain waves are differentiated by functions, locations, frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. Each brain wave has a different state in which they are able to function properly. To function properly, the brain waves must be in the correct location of the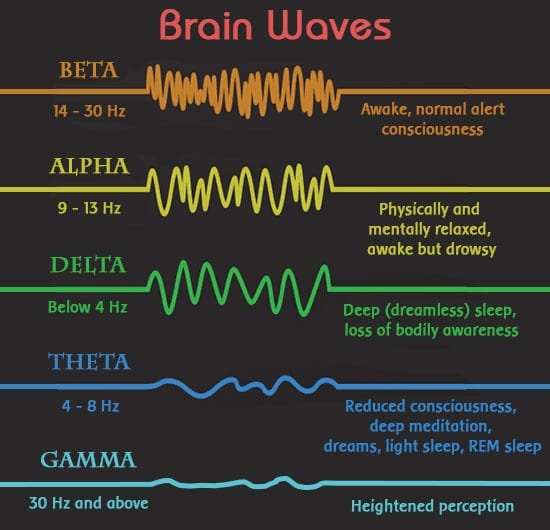 brain. Otherwise, the advantages might be substituted with disadvantages of all sorts. According to the book “I‑Minds: How Cell Phones, Computers, Gaming, and Social Media Are Changing …,” many creators/advertisements of video games state that they increase alpha/beta waves in your brain. However, not all locations in the brain are suitable for these brain waves. Thus, this can lead to multiple dangerous effects in the brain. Another component of brain wave differentiation is frequency or the number of crests are moving past any given point. The most common unit to measure frequency is known as Hertz (Hz). 1 Hz alias one crest per second. The frequency of a wave can be calculated by dividing the speed of the wave by the wavelength. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests. The final fundamental category is amplitude, or the maximum extent of the wave. These five classifications allow neurologists to determine the label of each wave.
brain. Otherwise, the advantages might be substituted with disadvantages of all sorts. According to the book “I‑Minds: How Cell Phones, Computers, Gaming, and Social Media Are Changing …,” many creators/advertisements of video games state that they increase alpha/beta waves in your brain. However, not all locations in the brain are suitable for these brain waves. Thus, this can lead to multiple dangerous effects in the brain. Another component of brain wave differentiation is frequency or the number of crests are moving past any given point. The most common unit to measure frequency is known as Hertz (Hz). 1 Hz alias one crest per second. The frequency of a wave can be calculated by dividing the speed of the wave by the wavelength. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests. The final fundamental category is amplitude, or the maximum extent of the wave. These five classifications allow neurologists to determine the label of each wave.
Infra-Low Waves – (lowest frequency)
When discovering waves by the order of frequency, Infra-Low brain waves come first. These waves have the lowest frequency-below 0.5 Hz. Because Infra-Low brainwaves have a very long wavelength, it is exceedingly difficult to study these waves. However, scattered information about these waves have been identified. Though there brainwaves have the lowest frequency, Infra-Low brainwaves are related to and affect other waves with higher frequency. Additionally, these waves appear to play an important role in the brain timing and network function. Thus, even the lowest frequency brainwaves can have unexpected results or effects.
Delta Waves – (low frequency)
The delta brainwave is present and functioning during the extremely deep, dreamless sleep one experiences after a long, exhausting day. The frequency of this wave ranges from 0.5 Hz to 4 Hz. Delta waves are essential to deep, dreamless sleep or the key to the power of healing. Delta waves are the most active during the first year and the last minutes of life (before death). The states when delta waves are the most active, result in production of “good” chemicals like growth hormones are produced. Thus, delta waves are essential for a satisfying rest.
Theta Waves – (medium frequency)
Theta waves are active when in very deep relaxation or meditation. However, in order to achieve this state, one must be extremely calm and absolutely silent. Although one is in deep meditation at this state, the human is still conscious of the surroundings. During this state, one may be dreaming with a light sleep, not as essential as delta sleep. The theta waves have a frequency ranging from 4 Hz – 8 Hz. The alpha-theta border ranges from 7 Hz to 8 Hz. Scientists have discovered many benefits of this range, such as the following:
- Relieves stress
- Facilitates deep relaxation
- Increases IQ
- Synchronizes the two halves of the brain
- Reduces pain
- Increase money
Alpha Waves – (medium frequency)
Alpha waves are created in your brain during light meditation and the peak of focus. These waves are also known as “ the sign of intelligence,” The flow of these waves increases imagination, visualization, memorization, learning, calmness, alertness, mental coordination and concentration. An interesting fact is that alcohol and other drugs increase alpha waves. However, an excess of alpha waves may turn into an inability to focus. The frequency of these waves typically range from 8 Hz to 12 Hz.
“ A new study by the University of North Carolina (UNC) School of Medicine recently identified the first evidence that a low dose of electric current of 10 Hz can enhance the alpha brain wave activity and boost creativity by 7.4% in healthy adults.”
-Christopher Bergland, “Psychology Today”
Beta Waves – (high frequency)
Beta brain waves flow through your mind during the states of alertness, activeness, decision-making and other activities that require quick thought processing. This is the most common state among adults. One who is highly engaged with their activity, such as a debater or a reality show host, would be most likely to be in the beta state. Although beta waves contribute to multiple everyday activities such as critical thinking, reading and writing, an uncontrollable amount can lead to stress and anxiety. Interestingly, coffee and other energy drinks increase beta waves.
These waves have a high frequency of 12 Hz to 40 Hz. There is one more important wave remaining with the highest frequency, yet one of the least known-
Gamma Waves – (highest frequency)
Gamma waves, alias insight waves, have unimaginably high frequency that include all brain waves above 40 Hz. This instantaneous motion makes this state a peak of mental and physical actions. Scientists have found that gamma waves are in all brains, but the quantity of it, varies in all brains. People with higher amount of gamma waves have been linked to higher intelligence whereas people with low amounts have been linked to learning disabilities like ADHD. How can I increase the number of gamma waves in my brain? The answer is pretty simple- meditate! Research has shown that monks or nuns have a higher quantity of gamma waves when meditating. Another study has shown that people who do extremely well in a specific activity, such as an Olympic athlete or Marie Curie, have a quantity of gamma waves exceedingly higher than those of average people. One more component that might help increase gamma waves is to love what you do!
This concludes our exploration of the waves in the brain.
Bibliography
- Academy, Mindvalley. “The Marvelous Properties of Gamma Brain Waves.” Mindvalley Academy – Ultimate Personal Growth Online University, www.mindvalleyacademy.com/blog/mind/gamma-brain-waves.
- Academy, Mindvalley. “This Is How Brain Waves Contribute to the State of Mind.” Mindvalley Academy – Ultimate Personal Growth Online University, www.mindvalleyacademy.com/blog/mind/brain-waves. Accessed 13 Sept. 2017.
- Bergland, Christopher. “Alpha Brain Waves Boost Creativity and Reduce Depression.”Psychology Today, Sussex Publishers, 17 Apr. 2015, www.psychologytoday.com/blog/the-athletes-way/201504/alpha-brain-waves-boost-creativity-and-reduce-depression
- “Infra-Low (ILF) Neurofeedback.” Infra-Low (ILF) Neurofeedback – UK, www.brainworksneurotherapy.com/infra-low-ilf-neurofeedback.
- “9 Things You Should Probably Know About Delta Brain Waves.” BinauralBeatsFreak.com, 8 Mar. 2016, http://www.binauralbeatsfreak.com/brainwave-entrainment/9-things-you-should-know-about-delta-brain-waves. Accessed 13 Sept. 2017.
- Swingle, Mari K. I-Minds: How Cell Phones, Computers, Gaming, and Social Media Are Changing Our Brains, Our Behavior, and the Evolution of Our Species. New Society Publishers, 2016.
- “ThetaHealing® Theta Brain State.” THETAHEALING, http://www.thetahealing.com/about-thetahealing/thetahealing-theta-state.html. Accessed 13 Sept. 2017.
- Mental Health, 15 Apr. 2014, www.mentalhealthdaily.com/2014/04/15/5-types-pf-brain-waves-frequencies-gamma-beta-alpha-theta-delta/.
- “What Are Brainwaves?” What Are Brainwaves ? Types of Brain Waves | EEG Sensor and Brain Wave – UK, www.brainworksneurotherapy.com/what-are-brainwaves.
- “What Is the Function of the Various Brainwaves?” Scientific American, www.scientificamerican.com/article/what-is-the-function-of-t-1997-12-22/.